Emission Reduction Programs
GC has conducted projects related to air pollution control efficiency both within its operating sites and surrounding area within the ensuring compliance with the standards stipulated by laws, regulations, and international practices. In addition, GC represents the petrochemical industry group in collaboration with government agencies to develop air pollution management guidelines. By applying advanced innovations, GC aims to maximize effectiveness through a strong working group network dedicated to environmental management.
GC has controlled NOx and SOx emissions from production process to be lower than the limitation that prescribed in the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report and Thai regulations. GC has developed programs to monitor NOx and SOx emissions in order to reduce impact to environment such as
- Using Continuous Emissions Monitoring System (CEMS) and periodically monitoring air emission quality by the certified external laboratories.
- Improving Gas Turbines and Low NOx Burners to reduce the NOx pollution emitted from its source.
- Adopting a policy for selecting raw materials and fuels, which have less impact to health and environment.
- Using low sulfur fuel oil and feedstock to reduce SOx emissions from combustion.
- Minimizing amount of fuel oil consumption to limit SOx emissions.
In 2024, highlights projects relating to improvement on control efficiency of air pollution include:
Control measures for Benzene and 1,3 Butadiene Sample
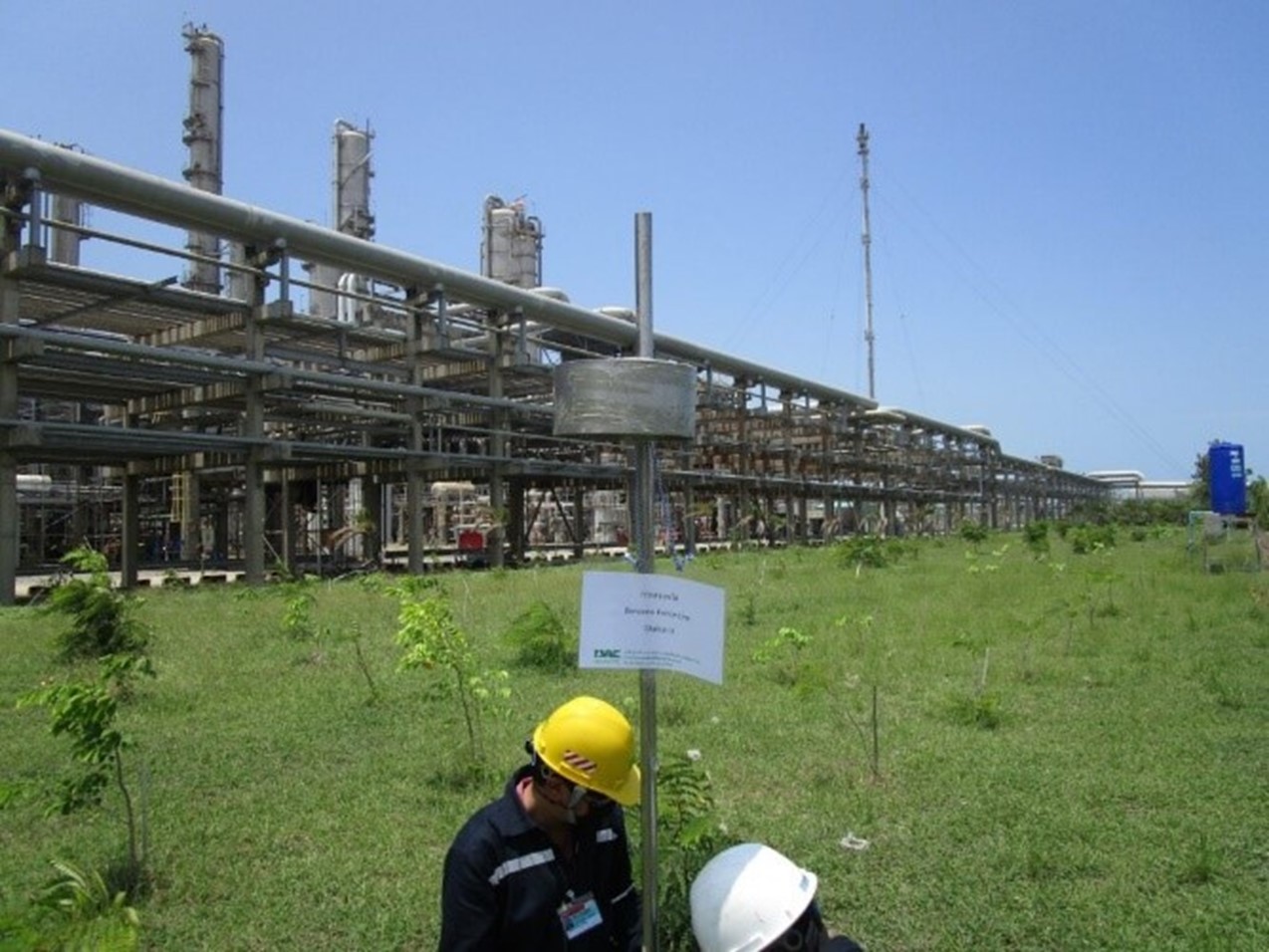
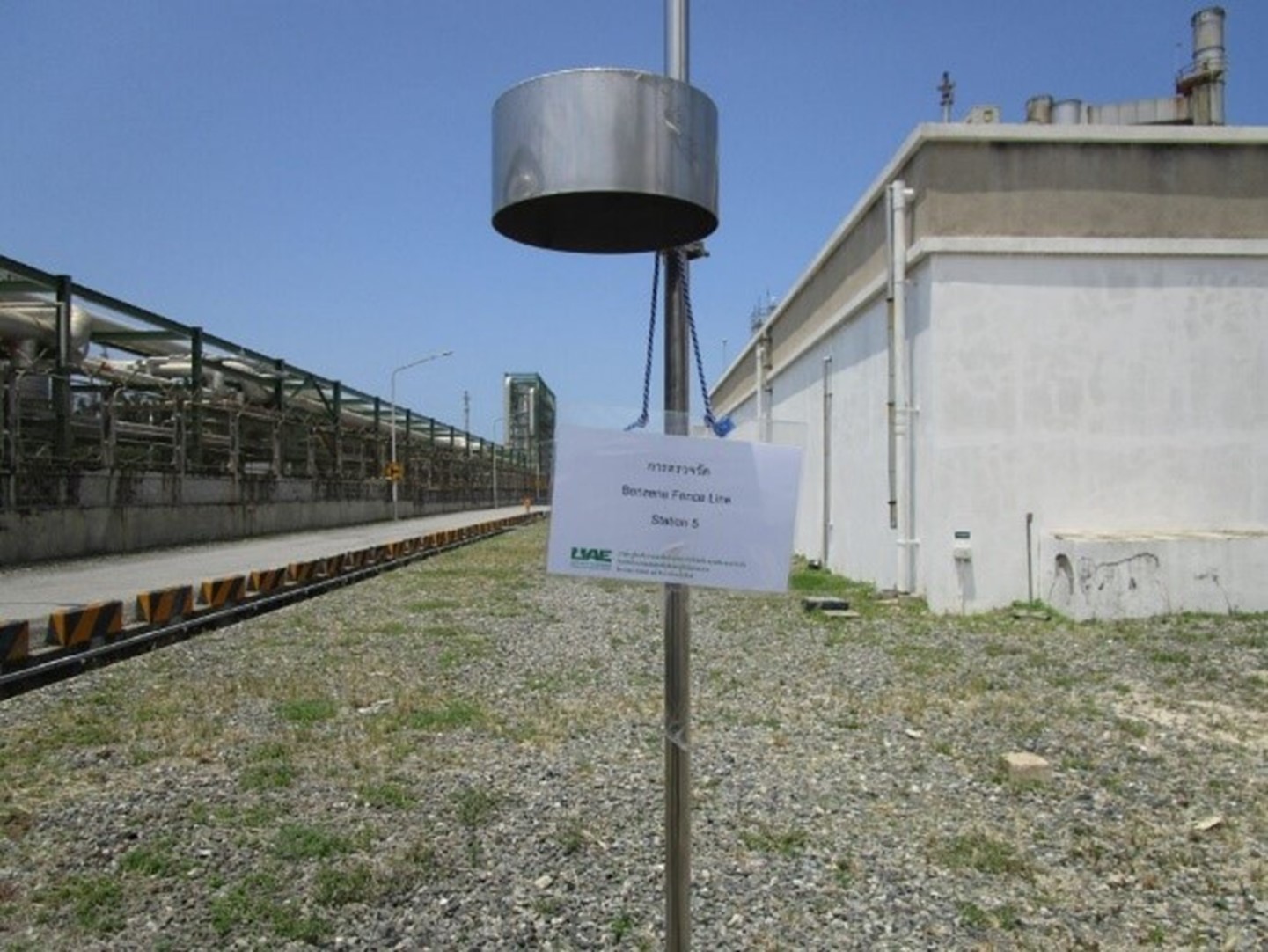


GC strictly complies with the Code of Practice (CoP) established by the Department of Industrial Works. This initiative is a collaborative effort between the Industrial Estate Authority of Thailand and the petrochemical industry group in the Map Ta Phut Complex, covering five industrial estates and one port.
GC has collected samples of benzene and 1,3 butadiene, in collaboration with Map Ta Phut Industrial Estate, to serve as a guideline for defining the standard monitoring value for benzene and 1,3 butadiene along the boundary. Testing locations have been assigned to cover areas along the plant’s fences and samples were collected in accordance with USEPA Method 325A and 325B standards in order to analyze the trend of air quality in the designated area. GC manages volatile organic compounds (VOCs) based on the Code of Practice. This will further lead to the definition of an appropriate standard value.
Predictive Emission Monitoring System: PEMs
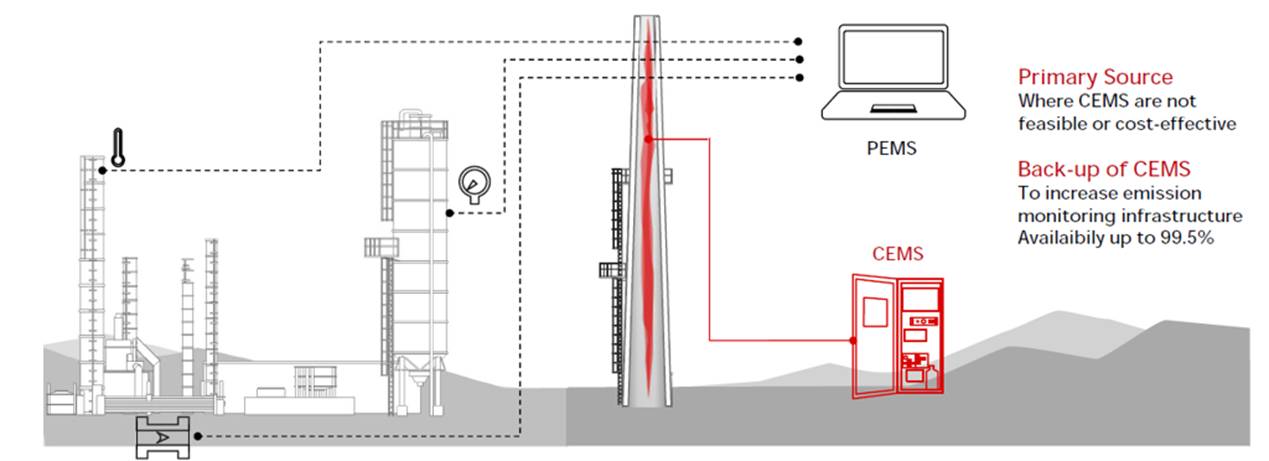
GC participates in the Petrochemical Cluster Working Group under the Federation of Thai Industries to explore alternative approaches for monitoring pollutant emissions. One such approach involves using chemical engineering principles to estimate emissions without drilling into flue stacks to install flow measurement instruments. This includes calculating key parameters such as sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon monoxide (CO). GC is studying the application of a Predictive Emission Monitoring System (PEMS), which uses mathematical models to estimate emissions from industrial processes. Data is collected from in-process sensors such as temperature, pressure, and fuel flow rate, instead of relying on direct pollutant measurements. This enables continuous monitoring, cost savings, and supports more efficient production process improvements.