Internal Water Management
GRI 303-1 (2018) 303-2 (2018)
GC has performed a review and analysis of operational processes that affect water quality, continuously monitored water usage estimates, and transparently disclosed water management performance and the likelihood of water impacts in consistent with the guidelines of international standards, e.g., CEO Water Mandate, ISO 14001, and national standards, namely Eco Factory Standard which encompasses water management guidelines, such as preparing inventories on water usage quantity, wastewater quantity and water balance, identifying activities that require the use of water and the amount of wastewater generated in each production process and other supporting activities of the organization. This also includes the formulation of an action plan and the implementation of measures to optimize water and wastewater management efficiency to achieve goals in an effort to maximize water use efficiency in production processes, recirculate water for utilization, and create cooperation along the supply chain. In doing so, emphasis is placed on efficient water use, adoption of innovation in water management, and water stewardship throughout the production chain, e.g., recycling wastewater from the treatment system, increasing water circulation cycles in the cooling system, etc.
GC has also conducted direct and indirect water use assessment throughout the Water Footprint of Product (WF) according to ISO 14046 and analyzed hotspots to maximize the benefit of water use, cut down water consumption in production processes, reduce freshwater withdrawal from natural water sources, and lower impact on water use from GC’s business operations.
Moreover, GC must define proactive measures, drive sustainable water management through the application of high technology to support the acquisition of additional water supply in an effort to ensure water adequacy for our existing productions, which is in line with water management actions in response to climate change, as well as to effectively accommodate future projects at reasonable costs.
GC establishes action plan to reduce water consumption in long-term and short-term including, 1) evaluate processes to identify opportunities for reducing water use without affecting product quality, 2) Introduce new technologies and strategies to optimize water consumption, and 3) regularly review and reassess water conservation effort to identify areas for improvement. GC has enhanced water efficiency in the production process, utilized renewable water, supported investment in water-related technology, streamlined production process, and sought alternative water supply, such as Sea Water Reverse Osmosis (SWRO) and Wastewater Reverse Osmosis (WWRO), etc.
Water Risk Management Programs
GC regularly conducts water risks assessment in water stress areas in terms of future water quantities available and future water quality-related risks, covering own operations, supply chain and product use phase, using the WWF Water Risk Filter tool.
Type of Site:
Own Operations (incl. subsidiaries)
(27 Sites)
Location:
-
Rayong, Thailand
(26 Sites)
-
Chon Buri, Thailand
(1 Site)
Type of Site:
Supply Chain
(7 Sites)
Location:
-
Rayong, Thailand
(7 Sites)
Type of Site:
Customer
(2 Sites)
Location:
-
Rayong, Thailand
(1 Site)
-
Samut Sakhon, Thailand
(1 Site)
Dependency-Related and Impact-Related Water Risk Assessment
GC conducts dependency-related and impact-related water risk assessments using the WWF Water Risk Filter tool, following WWF WRF guidance. The assessment examines both basin risk (water conditions around sites) and operational risk (site-specific water usage). This comprehensive approach helps identify water dependencies and impacts to guide targeted action plans.
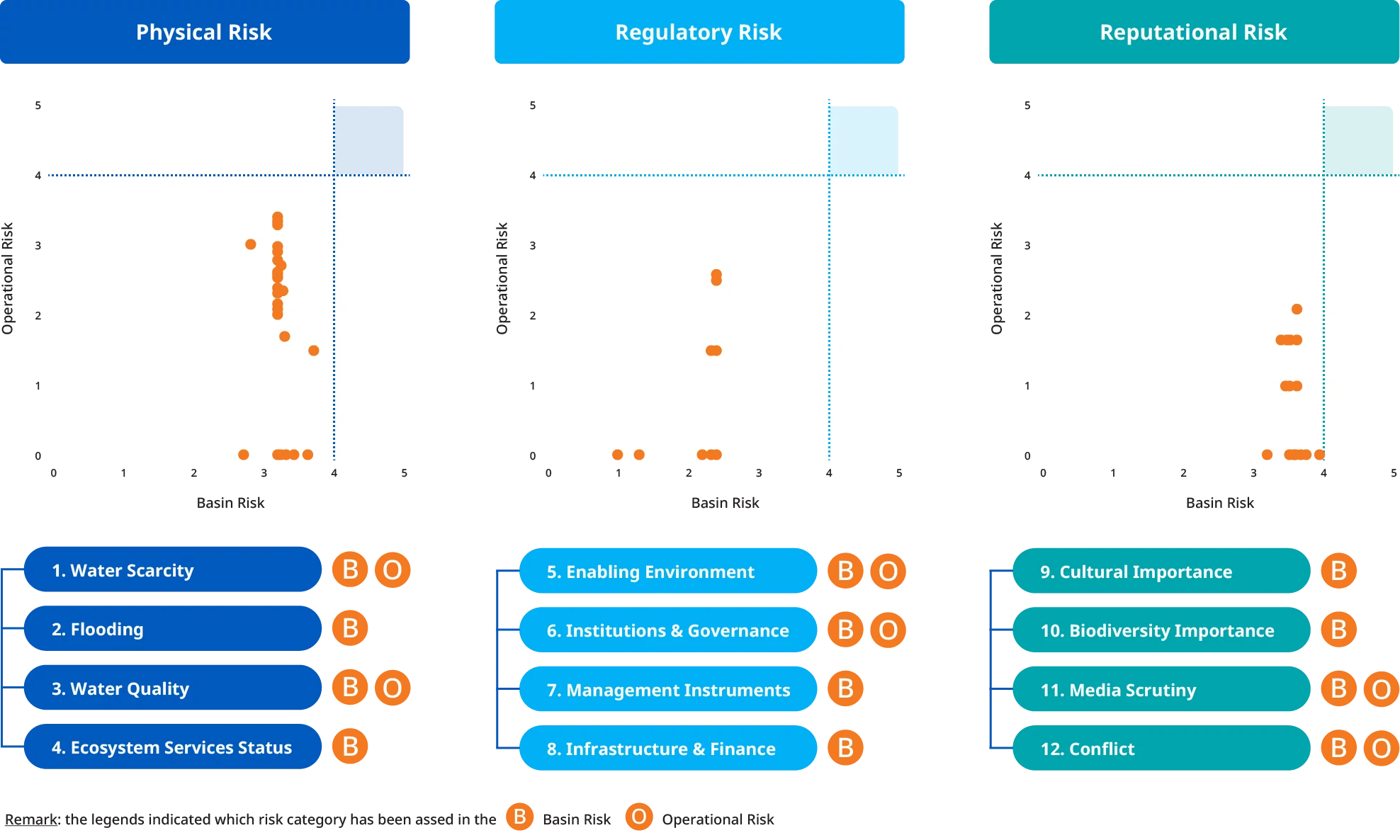
Based on the evaluation results, no operating areas were located in water-stressed areas. Upon considering and analyzing the assessment results of all three risk categories, namely physical risk, regulatory risk, and reputational risk, in collaboration with internal experts and external consultants, no production bases were assessed as high risk (Impact exceeding Level 4) in these three risk categories.
Future Water Quantities and Quality-Related Risk Assessment
GC assesses future water availability by analyzing water scarcity (the ratio of water demand to supply in each area) and assesses water quality through monthly monitoring at 14 points across Rayong (7), Chonburi (2), and Chachoengsao (5), measuring turbidity and conductivity. Additionally, GC collaborated with the Royal Irrigation Department and Provincial Waterworks Authority on water resource and reservoir development plans for Eastern Thailand, which is the main water resource supply to the company, ensuring sustainable water management to support future economic and industrial growth.
Impacts on Local Stakeholders Risk Assessment
GC places great importance on assessing risks of the impacts on local stakeholders by monitoring the water-related impacts of its business operations on both the environment and stakeholders in the area. This enables the company to identify potential issues and prepare appropriate mitigation plans. In addition, GC monitors local water quality to ensure its suitability for use and tracks local media (Media Scrutiny) to stay informed on concerns raised by local stakeholders regarding water issues. GC also participates as a representative in water-related committees to exchange perspectives and gain access to in-depth information from government agencies. This involvement contributes to building collaborative mechanisms at both the local and national policy levels.
Future Potential Regulatory Changes Risk Assessment
GC assesses future potential regulatory changes risks on the local level by collaborating with external organizations such as the Water Institute, major water users, and the local Keyman Water War Room under the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC). This collaboration allows the company to closely monitor water situations and regulatory changes. As a result, the company is able to track and evaluate future developments that may have a significant impact on its business operations.
Drought and Water Scarcity Preparedness
GC established the Water Management Task Force to manage water, monitor situations and plan actions to drive measures and execute long-term water crisis management based on three major water management guidelines, which are expected to reduce water-related costs, thanks to the plan to optimize water volume and cost, by approximately 90 million baht within 2025.
| Water Management Task Force | |
|---|---|
|
Optimize Volume |
GC performs an asessment of the entire production process to identify opportunities to reduce water use without affecting product quality by applying technology and innovation to increase production efficiency, decrease water consumption, and reutilize water for internal use to ensure sufficient water supply for business operations. GC regularly reviews operations and creates new knowledge to increase water conservation ability. |
|
Optimize Cost |
GC manages water resources with efficiency to maximize benefits and increases water resource portfolio to reduce costs and ensure stability. Furthermore, GC enters into long-term contracts with water service suppliers under appropriate conditions in terms of price and trading volume. The company takes into account suppliers providing better quality water at reasonable prices as an alternative to ensure water supply security. |
|
Monitor External Factors/Water Situations |
GC monitors both internal and external water situations while continuously asessing risks and potential impacts, e.g., regulations, water volume, water quality and water-related policies. The company also works closely with government agencies and individuals associated with water supply and demand management, promotes sustainable management practices across the supply chain, and communicates water management performance and accomplishments to all relevant stakeholders. |
GC has enhanced water efficiency in the production process, utilized renewable water, supported investment in water-related technology, streamlined production process, and sought alternative water supply, such as Sea Water Reverse Osmosis (SWRO) and Wastewater Reverse Osmosis (WWRO), etc.
Wastewater Reverse Osmosis (WWRO)

GC enhances the quality of reclaimed water using the Wastewater Reverse Osmosis (WWRO) system so that it can be reintroduced into the production processes. The project resulted in reduced water consumption by 213 m3 per hour, or 1.8 million m3meters per year from this project.
In 2024, GC conducted a feasibility study on the project to improve wastewater quality using the wastewater treatment system in the OLE4 site and Phenol factory, resulting in the reduction of wastewater discharged into public sources and the import of treated water.
Wastewater Reverse Osmosis (WWRO)
| Budget* | Reduction of Water Import* | Reduction of Water Discharged to Public Sources | Reduction of Expenses* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 46.5 million THB | 110 m2 per hour | 110 m2 per hour | 12 million THB |
*Note: Data from project forecasts once actual operations are conducted
Sea Water Reverse Osmosis: SWRO
GC has developed a project to produce freshwater from seawater to accommodate the company’s rising demand for water supply as well as prepare for drought crisis caused by climate change. GC also supports water management in the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) through the installation of the Sea Water Reverse Osmosis (SWRO) Plant which can reduce freshwater withdrawal from external sources by 3.02 million m3 per year.
Effluent Management
GC is strictly obliged to monitor its liquid discharges to maintain water quality at all production processes though the establishment and application of environmental policies and plans, namely QSHEB policy throughout the company to drive the environmental performance. We measure our quality of water discharges by complying with governmental environmental agencies and other international standards and obligations, such as Enhancement and Conservation of National Environmental Quality Act B.E. 2535. The Wastewater Discharge Requirements into the Central Wastewater Treatment System in Industrial Estates of Industrial Estate Authority of Thailand (IEAT) are also solely incorporated in the identification and measurement of pollutants. GC is aware of the impact of water discharges to the environment, so currently, the contaminated water was treated in the wastewater treatment to ensure the quality is always within effluent standard, the general effluent monitoring parameters are pH, temperature, COD, BOD, Total suspended solids (TSS), Oil and grease, and heavy metal e.g., Hg, As, etc.
Furthermore, GC also measures effluent discharge quality on a daily basis via an online system and reports to an internal working group to monitor and improve operational efficiency to ensure that the quality of wastewater released into water sources meets the legally required standard. In addition, GC inspects the quality of external water every two weeks to ensure that water sources surrounding the company’s operating sites is of good quality and will not produce any negative effect on the overall ecosystem. As a result of water quality monitoring in 2024, there were no cases regarding water quality exceeding standard requirements.