Supply Chain Management
Targets
- All suppliers acknowledge and comply with GC’s Supplier Code of Conduct.
- Green procurement of goods and services
- Supports local businesses and encourages the procurement of goods and services in the operating areas, to support local economy, employment and income distribution.
- Procure goods and services with honesty, integrity and fairness as guided by the company's governance principles.
Challenges and Opportunities
Efficient supply chain management can minimize business disruption risks which may directly affect the company’s business and image. It will also enhance operational efficiency and transparency as well as create shared values for both the company and suppliers. Therefore, GC has established a supply chain management strategy that promotes the mutual sustainable growth of the company, suppliers, and customers. GC’s supply chain management oversees an effective supplier selection process, assesses supplier risks and performance, directs and encourages suppliers to operate their business with environmental and social responsibility alongside corporate governance and in line with the Supplier Code of Conduct. The company also puts emphasis on supplier capacity development to prepare them for business growth in response to the rapidly changing global situations. Such effort will build confidence in working together and ensure the company’s ability to respond to stakeholder needs.
Management Approach GRI 3-3 (2021)
GC is committed to the management of an efficient supply chain that can support capacity building and continuous business expansions in accordance with the company’s growth strategy to ensure on-time delivery of quality products and services to customers. Furthermore, the company also aims to promote green procurement in addition to general procurement rules in order to gain customer trust and acceptance as well as create shared values for consumers and the society in our capacity as a leading chemicals business.
In order to create transparency, efficiency and traceability in our operations while also building confidence among all stakeholder groups across the supply chain, GC has assigned the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee, which is a Sub-Committee in the Board of Directors to define policies and oversee compliance with relevant laws, regulations, requirements, criteria and standards as well as create understanding and cooperation in procurement process development and investment expansion according to the company’s strategy.
Supplier Code of Conduct
GC has established the Supplier Code of Conduct to align suppliers and producers’ business practices with the company’s management guidelines. The Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee has been tasked to continuously review and improve the Supplier Code of Conduct so that it corresponds to business changes, covering issues on human rights and labor, occupational health, safety and environment, and business ethics.
Additionally, GC manages suppliers using a modern system that can constantly connect with suppliers in tandem with auditing their capacity and assessing their performance to ensure conformity with the Supplier Code of Conduct, which covers ESG issues. The company also places importance on working closely with suppliers to plan the procurement of replacement raw materials to enable business continuity in case of emergencies. Accordingly, meetings with key suppliers take place on a monthly basis. The meeting agenda covers both short-term and long-term raw material delivery plans, plant maintenance planning, performance, and corrective actions to be taken in case of problems.
Supplier Code of Conduct
Supplier Code of Conductof suppliers acknowledge and comply with the Supplier Code of Conduct
Supplier Screening
GC’s suppliers are categorized into feedstock suppliers, e.g., condensate and crude oil, and non-feedstock suppliers, which include contractors, machinery dealers, material and equipment dealers, waste management companies, freight forwarding companies, etc. GC’s major supplier is PTT Public Company Limited.
GC’s supplier selection process screens various dimensions of risks, such as risks related to products and raw materials in terms of strategy, procurement, price volatility and business competition risks related to governance, politics and laws of a specific location, and risks according to the industry, such as operational efficiency, resource consumption, pollution, and supply chain management, etc. Additionally, GC plans to include issues or performances related to ESG as parts of the criteria for supplier selection in the target group. For instance, consideration will be given to including management of climate change, such as target setting and decarbonization plans, as well as water management into the criteria. GC aims to apply these ESG-related criteria to non-feedstock supplier group, with plans to extend to feedstock supplier group in subsequent phases. Additionally, GC is in the process of incorporating ESG requirements, particularly those related to GHG emissions reduction and water management into supplier contracts and the Supplier Code of Conduct.
In addition to the abovementioned risk screening, GC’s suppliers must also pass an assessment which reviews their capabilities and qualifications in order to be included in GC’s Approved Vender List (AVL). The assessment uses the Vender Questionnaire and the Vendor Qualification Form which contain four risk assessment criteria, namely
1) Technical: Assessment of the supplier’s ability to comply with GC’s technical and project requirements.
2) Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC): Assessment of the supplier’s ability to guarantee the quality of products and services.
3) Safety, Health, and Environment (SHE): Assessment of the supplier’s competence in workplace safety, environmental responsibility and ethical principles.
4) Commercial: Assessment of prices, payment terms and the supplier’s overall commercial potential.
GC also prioritizes strong Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), including ethics, legal compliance and impact on the society. The weight of ESG performance is 25%, which reflects GC’s commitment to create a sustainable and responsible supply chain.
Vendor Qualification Criteria
Supplier Category Management
GC manages risks and prioritizes suppliers by using the Supply Positioning Model (SPM) to conduct spend analysis and risk assessment, covering risks on the company’s operations and ESG risks, in order to formulate a relationship management plan with each type of supplier. The company also monitors and audits supplier performance to further determine capacity development plans. Based on the spend analysis and supplier risk assessment, GC has classified Tier 1 suppliers into three levels including Strategics Supplier, Key Supplier and Manage Supplier in order to enable effective supplier relationship management (SRM) and enhance the procurement process:
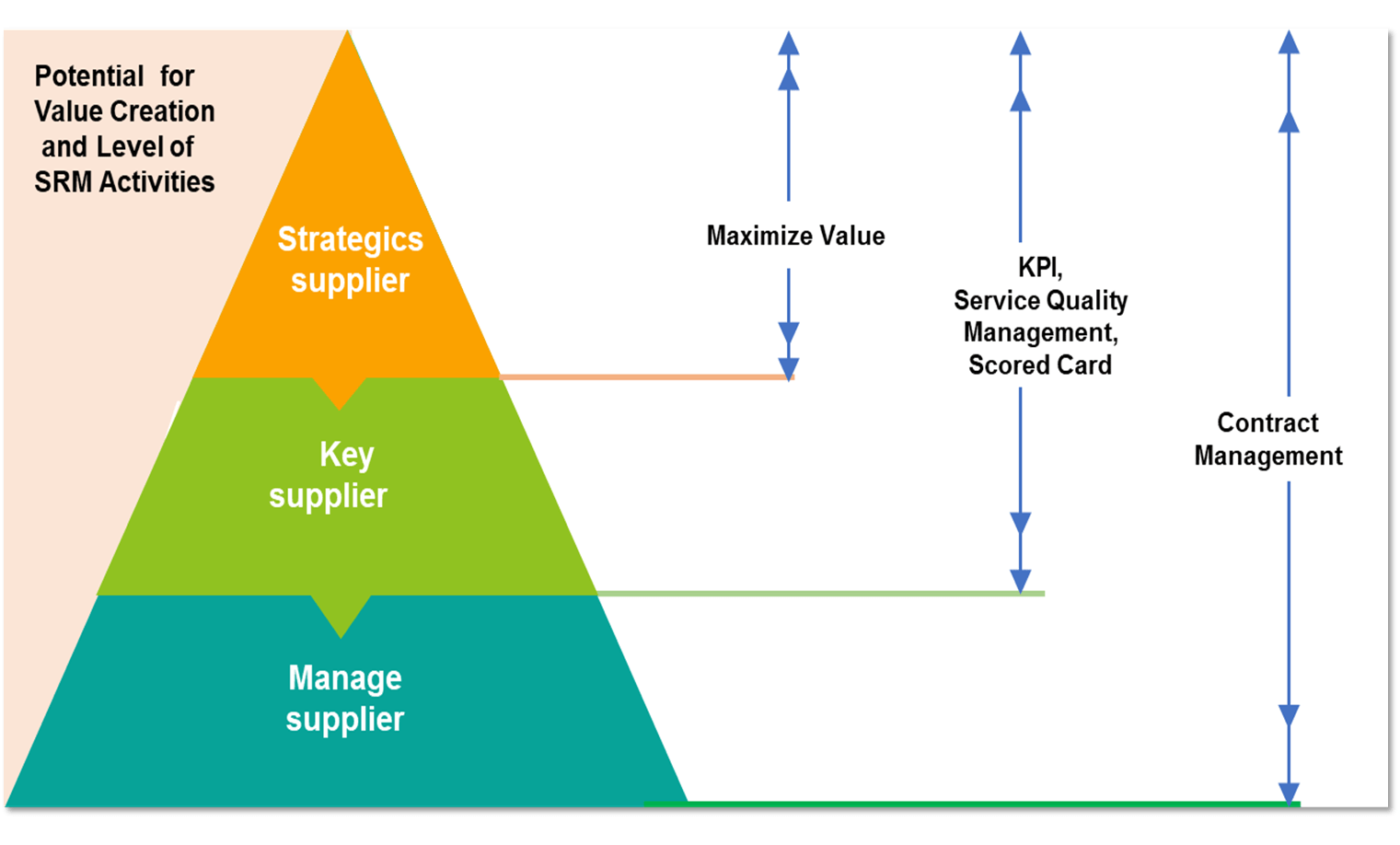
| Priority Level | Definition | Strategic Management | Management Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic / Significant Supplier | Suppliers that are of utmost importance to GC’s operations with high impact risks on themselves and on neighboring communities, which may produce serious impact on buyers in terms of business and corporate image | Developing relationships and aligning capacity enhancement towards the same direction in order to add value |
|
| Key Supplier | Suppliers whose activities are related to the distribution of products to consumers and contain high impact on buyers in terms of business and corporate image | Setting common goals to raise management quality |
|
| Managed Supplier | Suppliers whose activities are mostly operational and may impact neighboring communities or areas while posing low-to-moderate risks on buyers | Focusing on contract management to ensure that operations comply with specified conditions |
|
For Non-tier 1 Supplier, GC does not conduct direct ESG risk assessments for the purpose of supplier relationship management. However, ESG considerations for these suppliers are indirectly addressed through the oversight of Tier 1 Suppliers’ operations.
Supplier Assessment
GC implements a process that regularly and continually monitors, audits and assesses supplier performance through the Yearly Performance Evaluation to raise awareness among suppliers and ensure that they operate in adherence to the Business Code of Conduct, Supplier Code of Conduct, good governance principles, and relevant laws, with no environmental, social and governance (ESG) impacts. The process also supervises their compliance with international standards, such as ISO9001, ISO14001, ISO45001, etc. Such actions will result in mutual sustainable business growth. By conducting an ESG assessment, If a supplier is identified as a critical supplier with high ESG risks, GC will conduct a review and offer recommendations as well as explore opportunities to provide assistance to the supplier in order to improve and develop their operations for better ESG assessment results.
GC implements a thorough supplier assessment process based on standards and methods established in accordance with international standards. The assessment, which is performed in collaboration with experts in various fields, consists of both desktop assessment and on-site assessment.
- Desktop Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ): GC has implemented an international-standard supplier sustainability management platform for suppliers to conduct assessments and monitor sustainability performance, such as EcoVadis, which are used as tools to verify supplier’s operations.
- The company also conducts onsite audits by the company’s procurement staff or the purchasing agency using the ESG audit form namely “Supplier Sustainability Performance Assessment” and align with the company’s ESG framework and relevant international standards for the products or services in question. The company plans to utilize the assessment scores to benchmark ESG against peers toward enhanced sustainability practices.
- Supplier on-site assessment by third party is conducted in accordance with the international standards, such as assessment of labor standards (ISO 9001), environment (ISO 14001), health and safety (ISO 45001), and business ethics SMETA 4 Pillar, etc. The inspection for certification is conducted by the Management System Certification Institute (Thailand) (MASCI).
Furthermore, during the contract period or after its completion, the purchasing agency can make complaints and raise issues related to usage or ESG risks through the Vender Criticism process. In case of complaints against a supplier or a supplier not passing the assessment, GC will conduct an investigation, consider corrective actions, offer advice or suggestions, identify corrective or improvement measures and determine an appropriate timeline for the corrective action and means of jointly solving the problem with relevant parties before following up, verifying and re-assessing the case. However, if the supplier is unable to comply with the specified standards, the company will consider the temporary suspension of the purchase or the suppliers’ exclusion from our vendor list.
Example of suggestions or supplier corrective action/improvement plans include:
| Environmental | Suggestions or Corrective Action/Improvement Measures |
|---|---|
| Environmental Management |
|
| Social | Suggestions or Corrective Action/Improvement Measures |
|---|---|
| OHS Management |
|
| Human Rights |
|
| Governance & Economic | Suggestions or Corrective Action/Improvement Measures |
|---|---|
| Compliance with Laws and Regulations |
|
Supplier Assessment Result GRI 308-2, GRI 414-2
In 2024, GC conducted environmental, social and governance (ESG) audits with critical suppliers who completed the self-assessments. Consequently, no violations of labor rights, human rights, corporate governance, or the Business Code of Conduct were found. There were also no complaints related to human rights, ethics, compliance or the Business Code of Conduct through the company’s Vender Criticism channel.
Besides supplier assessment, GC also emphasizes on providing capacity development advice and support to suppliers who did not meet the criteria. The company has also developed supplier capacity building trainings to align operations across the company’s supply chain with the Supplier Code of Conduct and Sustainability Goals.
Additionally, GC recognizes the importance of applying digital technology and automation to strengthen and enable a rapid and accurate procurement process. This can facilitate employees while creating fairness for suppliers. For instance, the implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), an automated program that replaces employees in tasks such as issuing quotation requisitions, comparing prices, issuing Purchase Orders (PO), and submitting PO to vendors. The implementation of RPA resulted in the company’s improved procurement performance and reduction of operating costs. Accordingly, procurement has become more rapid, reducing working time and lowering the risk of feedstock shortage. Each and every step of the procurement process has also gained greater efficiency and offers traceability. Additionally, there are four other systems related to procurement:
- Vendor Management System (VMS): A management system used in the registration of new vendors and management of information on products and services included in the approved list.
- AI Spend Analysis: A tool used to analyze the procurement value for procurement planning.
- Smart Work Request: A system used to request service from contractors with annual contracts. This system replaces paperwork with an online format that can verify the number of work requests and costs in an accurate and rapid manner.
- New PO Tracking System: A system that tracks deliveries according to the PO.
GC has also launched the GC Procurement Chat BOT as another communication channel for communicating and answering suppliers’ questions in a rapid manner in order to cut down communication and work processes.